Economic trends for 2023 and beyond

Editor’s note: This article is part of an annual four-part series on trends impacting small and midsize businesses. In Part 3, we study economic trends for 2023.
We find ourselves at a unique intersection in history. We are consumed by daily reporting about the direction of interest rates, impacts on capital markets and the potential magnitude of a recession. This year’s economic trends will focus on the U.S. economy and variables such as growth, inflation, interest rates and the wage-price spiral.
Other 2023 trends
Part 1: Technology trends for 2023 and beyond
Part 2: Ecological trends for 2023 and beyond
Part 4: Social trends for 2023 and beyond
Special Report: The State of Employment and Wages
Economic outlook projections
As executive teams turn their attention toward 2023 budgets, some are asking how long high inflation, raw material shortages and the wage-price spiral will persist. The Federal Reserve’s projections suggest the Consumer Price Index (CPI) should return to about 4% by spring, but that higher interest rates will prevail for some time (the Fed will not reverse course on the countermeasure that arrests inflation).
A U.S. Federal Reserve Chair once described the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) as a host that “removes the punchbowl just as the party gets going.” That is, the Fed’s mandate is to smooth out variances in the business cycle. The Fed’s action of three successive 75-basis-point hikes is unprecedented. Here are the Fed’s projections on how interest rate hikes will impact the CPI:
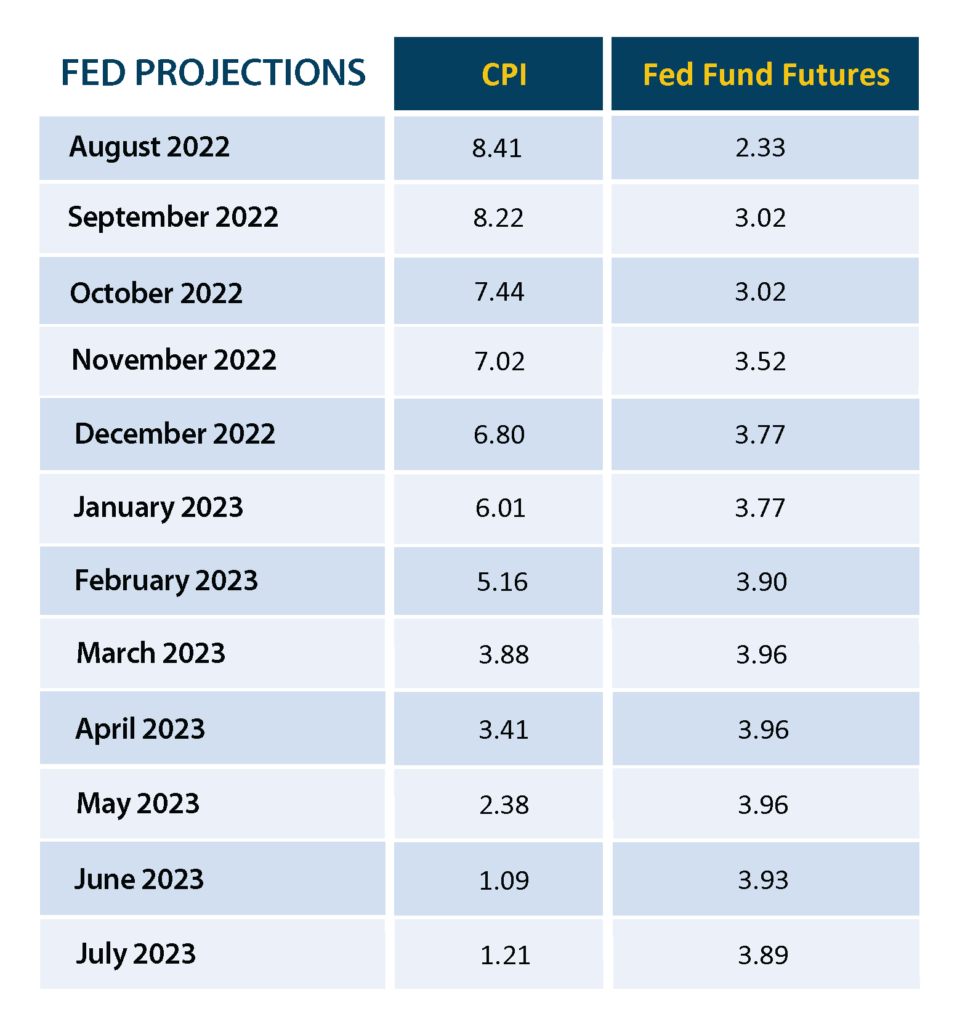
The classic definition of a recession is “a period of temporary economic decline during which trade and industrial activity are reduced, generally identified by a fall in GDP in two successive quarters.” The U.S. has already experienced two declining quarters. As has been well reported, a prolonged recession during a period of full employment and strong housing demand would be new territory. Yet whether the economy crosses this threshold may matter little to the roughly 60% of Americans living paycheck to paycheck.
Many economists describe 2023 as more of a “soft landing,” and the Conference Board expects a flat U.S. economy in 2023. The International Monetary Fund projects 1% growth — lower than some other advanced economies.
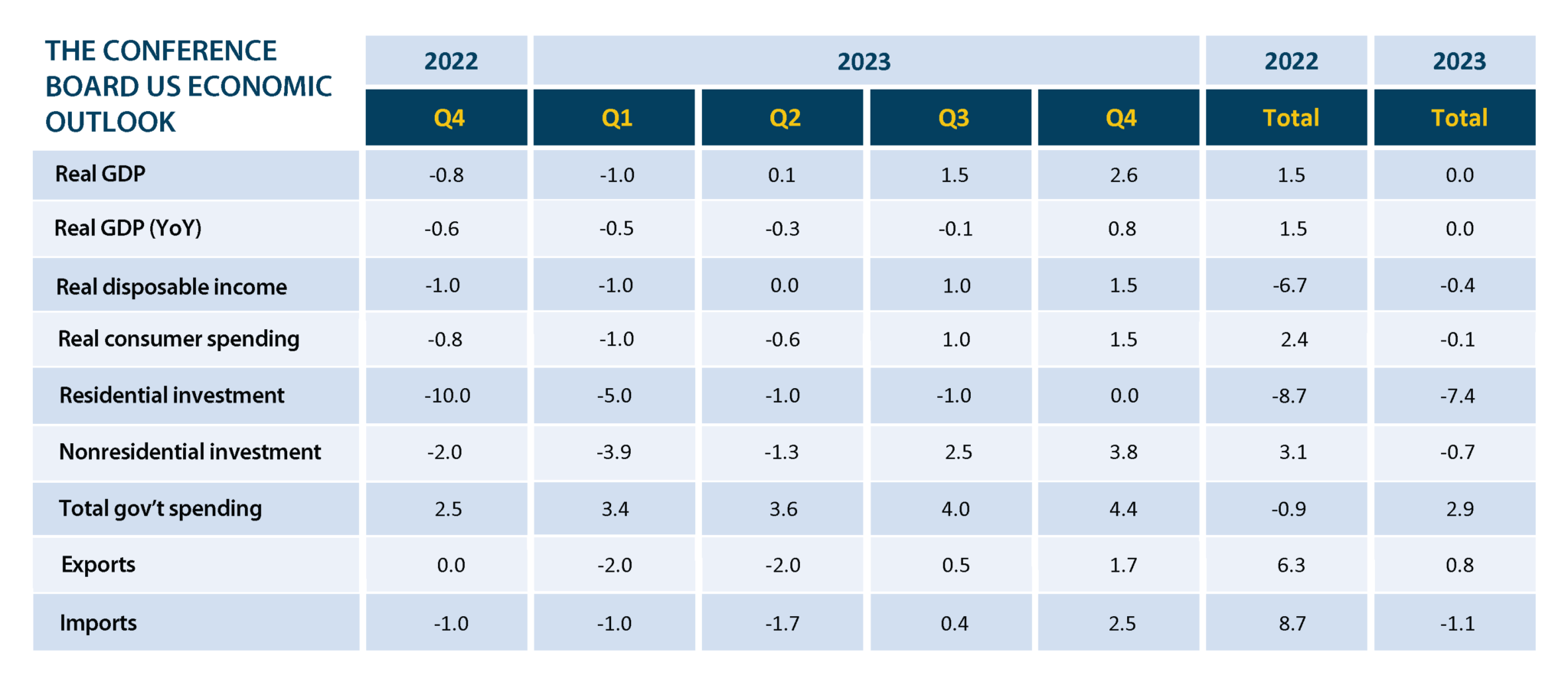
The fear for 2023-2024 is a prolonged period of stagflation (low growth coupled with high inflation). In 2023, we would expect tapering inflation in Q1 and Q2 — the primary variable being the Ukraine invasion or another unforeseen world event.
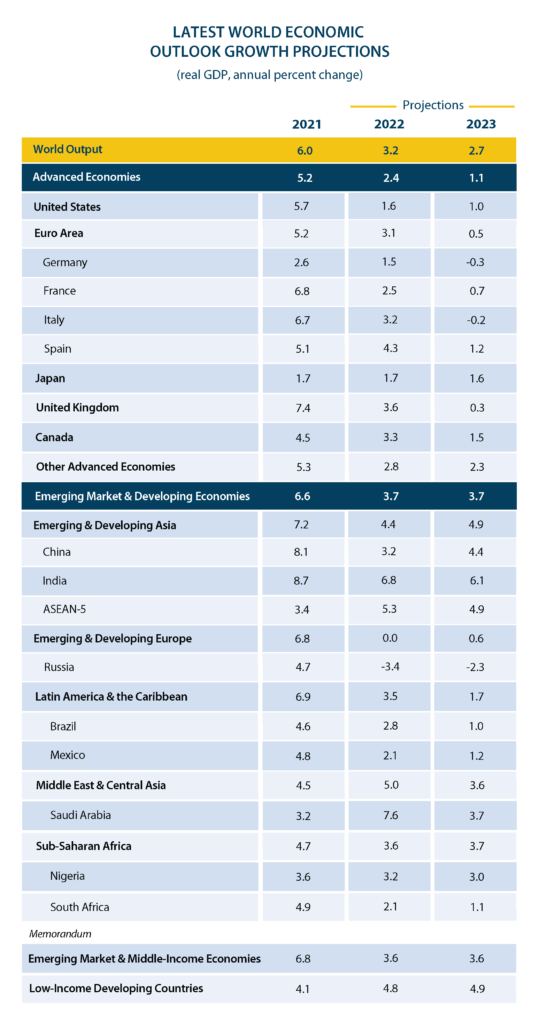
The most significant world events shaping our economic future include:
- The threat of a real estate meltdown in China, which appears already underway. The threat of a regional conflict in Taiwan or the South China Sea, higher global interest rates, ineffective vaccines, and COVID lockdowns have put China in an economic tailspin. i
- Three landmark bills on infrastructure, semiconductors and the environment will pump $1.7 trillion into the U.S. economy in the years ahead. While this is a needed investment, it represents a stimulus at a time when the Fed is trying to cool inflation.
- While the focus remains on the CPI, the Producer Price Index was up 8.55% in September from a year ago as U.S. companies grapple with high labor, energy and transportation costs.
- Inflationary pressure is worse in Europe than in the U.S. because of energy costs and the inability of central banks to apply a monetary policy with the same weight as the U.S. Federal Reserve. European governments are struggling to provide health and human services.
- Natural gas producers such as the U.S. and Canada have been unable to create suitable production to replace supplies from Russia. ii
- Every major currency has fallen versus the U.S. dollar. The Chinese yuan has slid dramatically in the last year.
- Several countries on the brink of default such as Sri Lanka, Ghana, Egypt and Pakistan have requested relief from the International Monetary Fund. iii
- The average American in the bottom 25% income quartile has 50% more cash than they did before the pandemic, which should put them in a better position to weather a downturn. Americans are saving in part because of poor consumer sentiment, even though they are earning higher wages and unemployment is low.
- As of this writing, major stock indices returned upward during a wild earning season that included a flight toward safety and away from technology stocks that often perform poorly when impacted by higher borrowing costs.
- Manufacturing is showing softness given high wage rates, delays in automation, supply chain shocks, and moderating demand.
How the Federal Reserve will manage stagflation and the wage spiral
The Fed’s balance sheet and its willingness to use it set the U.S. apart from other advanced economies.
Yet, the Fed finds itself in a tenuous position as it tried to achieve equilibrium — an ideal state known as NAIRU (non-accelerating inflation rate of employment). NAIRU is a theoretical state where the U.S. economy is at full employment but not producing inflation. While the term “full employment” has been associated with a 4% unemployment rate, the Fed appears poised to tolerate unemployment at 5-5.5% to moderate inflation.
The Fed’s policy is rooted in history and its failures of the past. Until the 1970s, economic theory held that rising unemployment would curtail rising wage inflation (Phillips Curve). iv Yet the 1970s represented a coexistence of high inflation, interest rates and unemployment. The confluence of these conditions was stagflation, a cycle that is hard to break. It’s what some economists refer to as a state of “stable disequilibrium.”
During that unique time in history, the Fed learned that the fear of inflation was worse than inflation itself. That is, inflation psychology can become self-perpetuating. What made for a uniquely serious economic condition was that the inflation was driven by supply chain shocks (most notably an embargo on oil from OPEC). When workers fear inflation because they can’t buy goods at all — supply chain disruption — they buy goods earlier (driving up prices) and switch jobs more readily, creating a wage-price spiral. Supply shocks are harder for the Fed to manage through monetary policy than demand shocks.
There is already evidence of a softening wage-price spiral. As we suggest in our special report, The State of Employment and Wages (posting next week), the curve of wage inflation (mean of 8%, and 16% for job switchers) is starting to flatten.
Not your grandfather’s yield curve
It’s well known that inverted yield curves are an indicator of a pending recession 10 to 11 months in the future. Yet the mechanics of the yield curve are less understood.
The premise is that long-term debt bond instruments such as treasury bills should offer higher interest than short-term instruments. An inverted yield curve occurs when long-term treasury yields drop below the yield of short-term treasuries. This reflects a sentiment where investors are more confident in the short term than the long term.
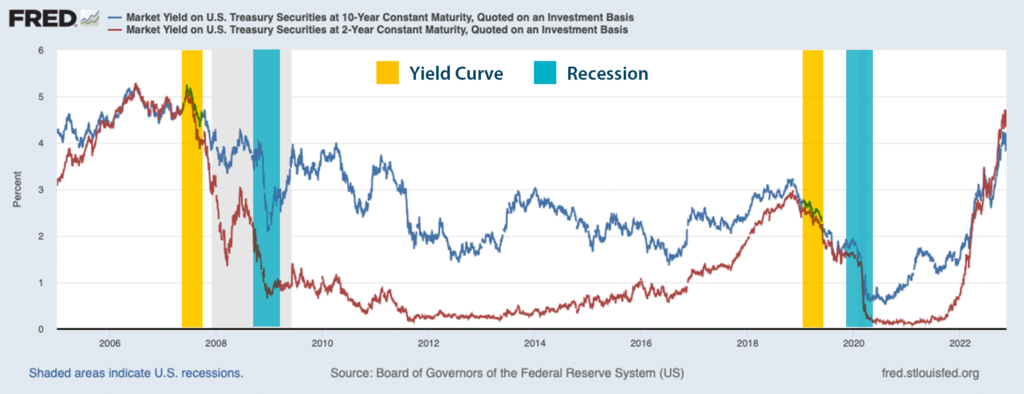
But the current circumstances are very different than those in recent history. Inflation is distorting the yield curve since more return is required by investors as the cost of their money deteriorates. For this reason, some economists believe the current inversion is not the precursor to a significant decline in GDP.
Economic detente with China
The press stokes fear about global conflicts, from missiles launched in North Korea to Iran’s nuclear aspirations and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Yet, in the long term, it’s America’s rivalry with China that presents the greatest threat to America’s economic dominance. In the short term, China is struggling, with projected 2023 GDP growth at a tepid 4.4%. The Biden Administration does not seem enthused about rolling back Trump-era trade protections and tariffs that put the Chinese on notice of America’s resolve regarding trade policy.
As we suggested last year, globalization will be taking on a new form: the world split into two economies — East and West. The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework attempts to reduce dependence on China. The World Trade Organization has cited a significant slowdown in global trade as a result of high transportation costs, rising interest rates and regional conflicts.
Some imports from China will be hard to unwind, but the potential for conflict in Taiwan and the South China Sea only reinforces an inherent lack of cooperation between the U.S. and China. Long before the Ukraine invasion, U.S. companies had been de-risking their supply chains, and recent COVID disruptions in China are only amplifying the importance of self-reliance within the supply chain.
Industry updates v
Automotive
Global demand is expected to rise 0.9% as consumers are squeezed by inflation and producers struggle to meet demand amid severe supply chain disruptions. North American new car sales are expected to decline by 2.4%, while EVs continue to dominate new product introductions, soaring to five times their pre-pandemic production level.
Financial services
The whole retirement plan industry is under serious stress as U.S. pension plans are funded based on invalid growth and inflation assumptions. The prospects for large pension plans or governments that sponsor them to fail could spark a meltdown. Banks are under fire from fintech and cryptocurrencies, and insurance agencies are dealing with the financial aftermath of Hurricane Ianm which will result in roughly $67 billion in losses. vi
M&A set records in 2021 after the COVID-induced slowdown. Deal flow was worth $995 billion in the first half of 2022, down 29% from the prior year. Private equity firms make up about 40% of activity, as they rely heavily on leveraged loans and high-yield bonds to complete transactions. Deals will be expensive to finance, putting pressure on near-term valuations.
Energy
The energy sector remains in a state of flux. While natural gas prices fell by 40% in recent months, imbalances have forced the industry to reverse course back toward fossil fuels including coal.
See our 2023 Ecological Trends report for more on energy.
Health care
The health care sector is under significant strain as inflation outpaces growth, which is likely to result in insurance companies cutting benefits while dealing with the pandemic’s aftermath. Governments are putting pressure on pharmaceutical providers to cut prices.
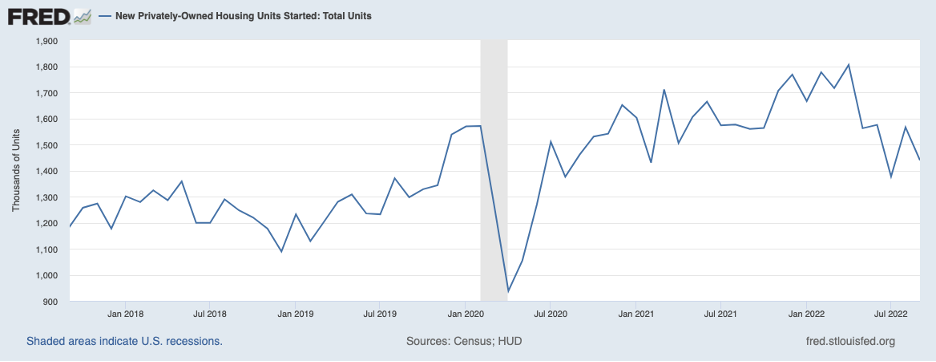
Housing starts and construction
Housing starts were down 6.1% for the year. In addition to soaring interest rates (the highest since 2002), the sector has been slowed by persistent raw material cost increases. Mortgage applications are down 40% since January. Multifamily (more than 5 units) also dropped 13% in September.
Construction companies often try to flex back and forth during up and down cycles. Projects have been funded by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. Infrastructure projects will grow 20% in 2023, perhaps the beginning of an industry reset amid a sharp decline in housing starts. vii
Retail
Retailers are in a mad rush to embed technology into their stores to automate, implement contactless payment systems such as Apple Pay and Venmo, and utilize augmented reality to perpetuate self-service. E-commerce and omnichannel are more mobile-ready — enabled by better broadband and 5G. Additionally, there will be 79 million buy-now-pay-later shoppers in 2022, up 56% for the year. The bar has been also raised to same-day delivery. Discounters such as TJ Maxx, Burlington and Dollar General should fare well in an inflation-rich environment.
Technology
Large technology stocks are in a slump. The NASDAQ has performed poorly versus the S&P in recent weeks, in part because of skyrocketing borrowing costs, tighter regulation, and poor performance by Meta and others who have not realized the benefit of the metaverse and other emerging technologies.
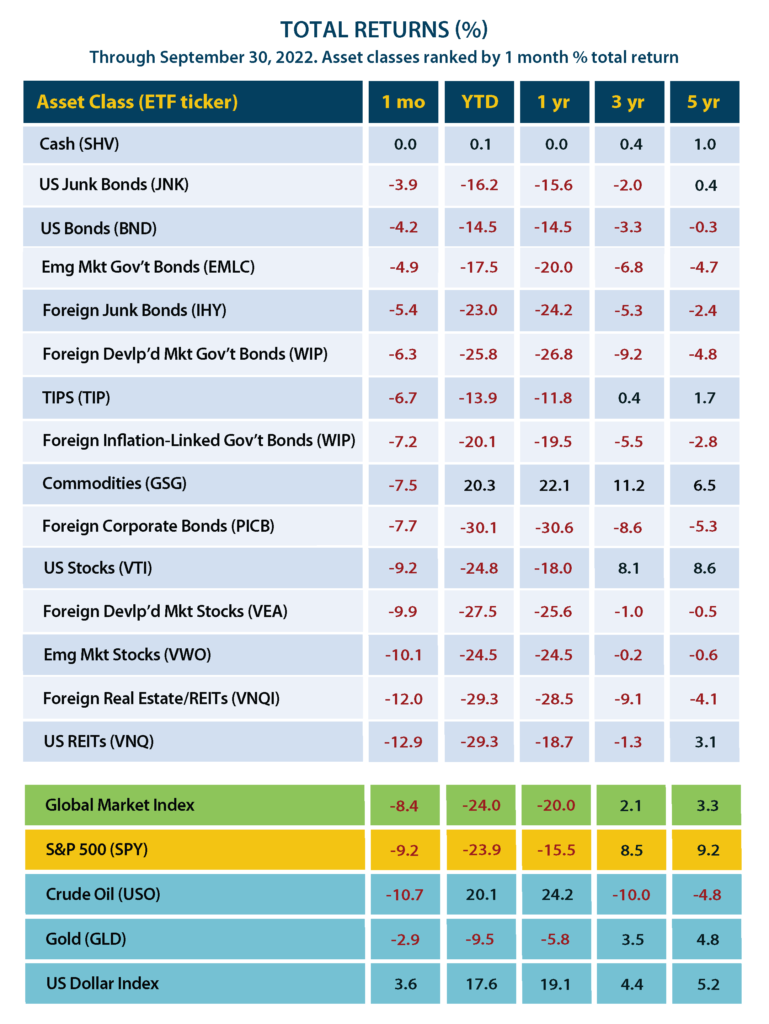
Asset class wars
Crypto winter hit the sector hard. The collapse of FTX shocked Wall Street and shook the confidence of mainstream investors. Bitcoin peaked last November at $67,000, or about $3 trillion in market value. It then slid to less than $20,000 amid perceptions that crypto felt more like a Ponzi scheme. Yet it seems many corners of our economy stand to benefit from blockchain’s potential to act as a distributed ledger for all types of activities, from trading real estate to credit scoring.
Investors have had a frustrating 2022. In a year where leaving money in cash provides little resistance to inflation, investors had few options with everything from commercial real estate to gold performing poorly. Some recovering sectors including retail real estate and oil are inflated by OPEC production cuts.
Let’s hope that 2023 will provide a stable environment for investors, businesses and their employees. While the focus is on a potential recession, a better description might be that we are entering a new stage of the business cycle, marked by high-interest rates and low growth. Perhaps our fear should be less about GDP decline and more about the persistence of stagflation. Yet the Fed is signally it is resolute in disrupting the wage-price cycle.
As companies plan for 2023 and beyond, they must be particularly thoughtful about when and where to push their chips to the middle of the table.
References
i Kiplinger Letter Vol. 99, No. 39
ii Mauldin Economics
iii Kiplinger Letter Vol. 99, No. 40
iv 21st Century Monetary Policy by Ben Bernanke
v Industry Outlook in 2023 – Economist Intelligence Unit
vi RSM and the Insurance Journal
Related Resources
Jan 13. webinar: Trends for 2023 and beyond [Register in the blue box]
Mergers & acquisitions trends for 2022
Trends facing business in 2022 and beyond
Category : Economic / Future Trends

