Why digital transformation is a matter of survival

As new competitive realities emerged during the pandemic, many companies embraced digital transformation. Most adopted tools such as Teams, digital payments and marketing automation to improve productivity.
However, digital transformation can’t be viewed in an incremental, linear fashion. Siebel founder Thomas Siebel refers to digital transformation — the confluence of cloud computing, big data, artificial intelligence and the internet of things (IoT) — as a “mass extinction event.”
Entire industries and businesses will either adopt these technologies, or be eliminated.
By reaching critical mass, the interconnectivity of billions of devices will drive the value created through big data and advanced analytics.
The bridge we must cross is from levering technology to improve service or reduce cost, to utilizing digital transformation to redefine our core product in a way that creates new demand and drives enterprise value.
Consider the case of an orange farmer. His core product has been found in nature for thousands of years and is a commodity.
What if the seeds he uses to grow oranges could be selected for ultimate flavor and yield by AI, planted and picked by autonomous vehicles, harvested at the ideal time based on moisture, heat, sunlight detected by IoT sensors, and sold at the highest market price based on advanced analytics?
While the product may be ostensibly the same, the grower would be far more competitive and profitable, and would deliver a superior product using tools that are already commercially available today.
We must leverage these tools now, or face the consequences. Here are 4 ways digital transformation is taking form:
1. Cloud computing is a shared pool of configurable hardware.i
In recent years, cloud solutions have become more “virtualized,” enabling greater hardware efficiency.
As a result, leading providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) have been successful in compartmentalizing their solutions in the form of hybrid clouds (a combination of on-premise infrastructure and public cloud), which offer greater security, agility and speed.
Cloud computing costs have dropped over 60% in the last two years. While cloud computing is the host of digital transformation, our understanding of it is only scratching the surface.
Metcalfe’s Law dictates that the power of any network is the square of the devices sitting upon it. That is, as IoT devices and networks are combined with other networks, they become infinitely more powerful.
For example, the integration of CRM and ERP systems make each of them much more valuable.
When Facebook started at Harvard, its value was contained, but when it spread to other schools (network effects), its power was unleashed.
2. Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines.ii
Artificial intelligence (AI) will either amplify America’s standing as an economic superpower, or it will allow China to propel ahead of us.
As pseudo-government controlled companies operate there, Chinese companies could gain a foothold on AI technologies. Siebel points to the following commercial use cases of AI:
- Financial services: Fraud detection, credit analysis and scoring, loan application review and processing
- Healthcare and medicine: Medical image diagnosis, automated drug discovery, disease prediction, genome-specific medical protocols, preventative medicine
- Manufacturing: 3D customization, inventory optimization, predictive maintenance, quality assurance
- Oil and gas: Predictive oilfield and well production, well production optimization
- Public safety: Threat detection
- Military: Predictive maintenance to improve readiness and streamline operations, logistics optimization, inventory optimization and recruiting. AI has proven remarkably useful in improving predictive maintenance for the U.S. Air Force and improving aircraft readiness.
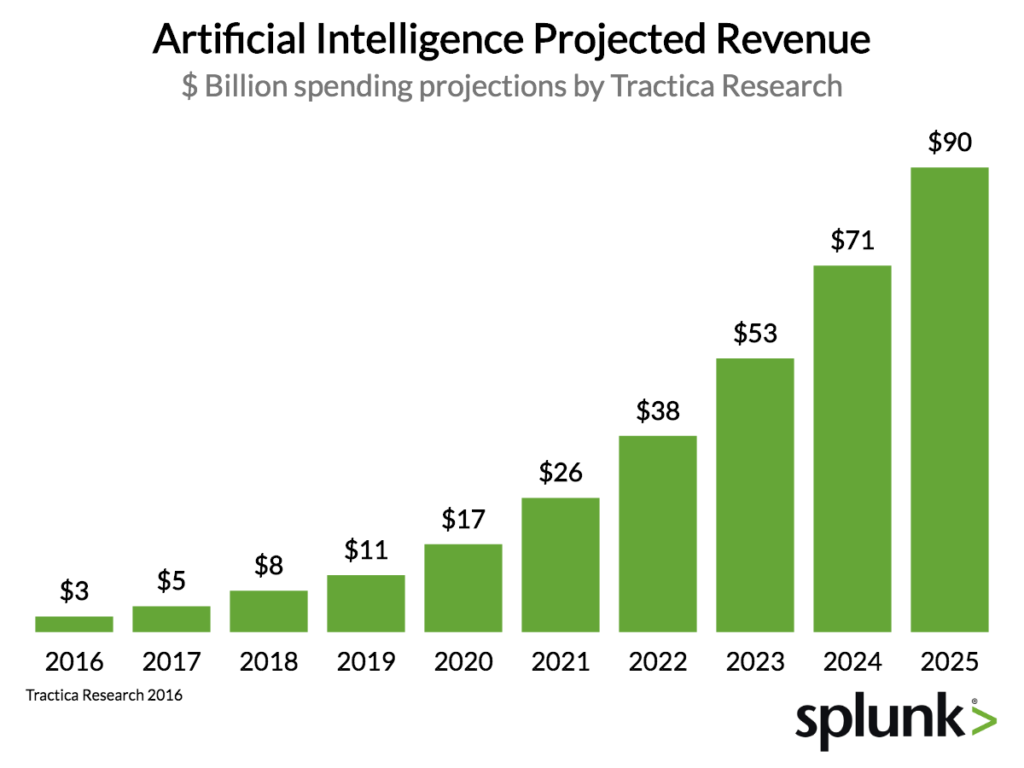
Source: Tractica Research
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence. Machines learn from examples and experience, which are different from hard-coded rules typically found in AI. Machine learning will predict future results instead of just reporting them.
3. Big data is comprised of complexly structured and unstructured data sets that are rapidly generated and transmitted from a wide variety of sources.iii
Big data represents the intersection of volume, velocity and variety from both internal and external (extraprise) data sources.
For example, our firm did strategy work with a Vistage member who loaded Walmart scan data and Best Buy movement information into their Microsoft Power BI data visualization solution, which augmented their internal data.
Their system provided real-time analytics that allow them to predict future events and manage their supply chain with greater precision.
This technology is neither expensive nor hard to implement. In our consulting practice, we see a sea change underway, where members are not satisfied with the reporting of static data, they want to convert that data into actionable insights.
4. The Internet of Things (IoT) is the sensoring of the entire value chain though remote access.iv
IoT is being framed by the entry of high-volume, low-cost chips. By 2030, it is estimated there will be a staggering 75 billion IoT devices deployed worldwide.
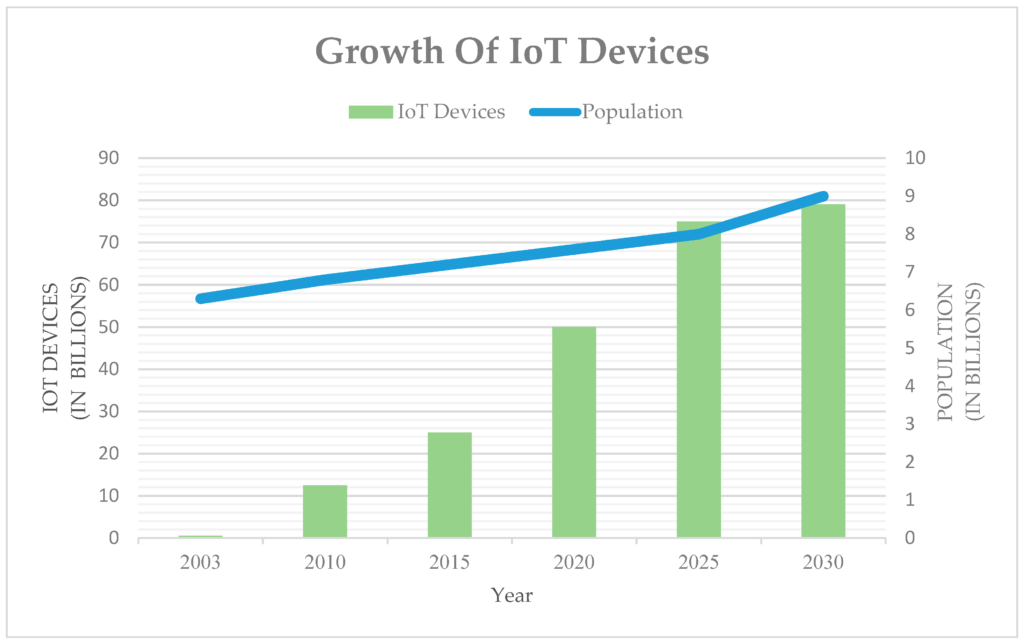
Source: MDPI
IoT will provide the greatest value to industries with high asset costs. 50% of IoT investment is projected to be made in manufacturing, transportation/logistics, and utilities.
Deep learning will provide richer analysis than previously possible. 5G cellular networking will enable a new generation of IoT devices such as smart grids, smart cities and autonomous vehicles.
The combination of these solutions will make us safer, increase accuracy, and save on labor costs and administration.
Where do you start?
Providers should map their entire value chain and look for opportunities to deploy digital transformation strategies. Below are examples of value chain elements that could be deployed for a manufacturing business:
- Suppliers: Inventory optimization, supply network optimization
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance, quality assurance, 3D manufacturing, safety
- Customer: Customer service (chatbots), customer insights and analytics, warranty optimization
- Distributor: Inventory management, price optimization, quote optimization
- Logistics: Demand planning and forecasting
As noted, our observation is that private companies are acting more like observers of change. Clearly, larger public companies are better equipped to invest in expensive technologies such as AI.
Yet, there are many emerging providers offering software-as-a-service, platforms as a service, infrastructure as a service and artificial intelligence as a service. Renting software also eliminates the need for costly cap-ex investment.
As digital transformation technologies become more accessible to private companies, it is incumbent upon us to be prepared to take advantage of them.
References
i Digital Transformation by Thomas Siebel
ii TechTarget
iii What is Big Data? How Does it Work? [Built In]iv Digital Transformation by Thomas Siebel
Related Resources
Technology trends facing business in 2022 and beyond
Marketing Matters: Responding to Changes in Buyer Behavior
Category : Strategic Planning

